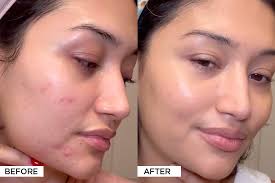
Hormonal acne, often characterized by deep, cystic breakouts primarily around the jawline and chin, can be a frustrating and persistent condition for many individuals. While various treatment options exist, Accutane, also known by its generic name isotretinoin, is often considered a last resort for severe cases of acne, including those influenced by hormonal factors.If you are looking for some genuine cure then must try isotretinoin 40 mg
What is Accutane?
Accutane is a potent oral medication derived from vitamin A, belonging to the class of retinoids. It is primarily used to treat severe, treatment-resistant acne that hasn’t responded to other conventional therapies. Accutane works by targeting multiple factors contributing to acne formation, including reducing sebum (oil) production, preventing the clogging of hair follicles, and combating inflammation. You can also buy isotretinoin online
How Does Accutane Address Hormonal Acne?
Hormonal acne is often driven by fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly androgens such as testosterone. These hormones can stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce excess oil, leading to clogged pores and the development of acne lesions. While Accutane does not directly regulate hormone levels, it effectively addresses the downstream effects of hormonal imbalances by:
1. Reducing Sebum Production:
Accutane significantly decreases the production of sebum by the sebaceous glands, which is often elevated in individuals with hormonal acne. By reducing oil production, Accutane helps to prevent the formation of acne lesions and promotes clearer skin.
2. Preventing Microcomedone Formation:
Microcomedones are the precursor lesions of acne, formed when hair follicles become plugged with excess sebum and dead skin cells. Accutane helps to normalize the process of keratinization within the follicles, preventing the formation of microcomedones and subsequent acne lesions.
3. Suppressing Inflammation:
Hormonal acne is often characterized by deep, inflammatory nodules and cysts. Accutane has potent anti-inflammatory properties, which help to reduce the size and severity of existing acne lesions and prevent the formation of new ones.
4. Promoting Skin Renewal:
Accutane accelerates the turnover of skin cells, leading to faster healing of acne lesions and overall improvement in skin texture and appearance. This accelerated skin renewal process helps to prevent the formation of acne scars and hyperpigmentation associated with hormonal acne.
Considerations Before Taking Accutane:
While Accutane can be highly effective in treating severe acne, including hormonal acne, it is not without risks and considerations. Before starting Accutane treatment, individuals should:
– Consult with a Dermatologist:
Accutane should only be prescribed and monitored by a qualified dermatologist experienced in its use. A thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, acne severity, and potential risk factors is essential before initiating treatment.
– Undergo Regular Monitoring:
Regular follow-up visits and laboratory tests are necessary throughout Accutane treatment to monitor for potential side effects, including elevated liver enzymes, lipid abnormalities, and teratogenic effects (harmful effects on fetal development).
– Use Effective Contraception:
Due to the teratogenicity of Accutane, strict contraception measures are mandatory for sexually active women of childbearing age. Pregnancy must be avoided during Accutane treatment and for at least one month after discontinuation.
– Be Aware of Potential Side Effects:
Accutane can cause a range of side effects, including dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, photosensitivity, muscle and joint pain, mood changes, and rare but severe complications such as inflammatory bowel disease and increased intracranial pressure.
Conclusion:
Accutane, with its potent anti-acne properties, plays a crucial role in the management of severe, treatment-resistant acne, including cases influenced by hormonal factors. By addressing key components of acne pathogenesis, such as sebum production, follicular hyperkeratinization, inflammation, and skin renewal, Accutane offers significant improvement in acne severity and quality of life for many individuals. However, careful consideration of its risks and benefits, along with close medical supervision, is essential to ensure safe and effective treatment outcomes. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide personalized guidance on the use of Accutane for hormonal acne and help navigate its complexities effectively.


